"The greatest threat to our planet is our belief that someone else will save it."
The Kariega Game Reserve Protected Area is managed in accordance with a Habitat and Wildlife Management Plan, drafted in accordance with the most current conservation research and laws.
While our intention is to let nature take it's course, there are certain 'at risk' species that require strategic conservation management, in some cases to save the species from extinction and in other cases to maintain the genetic integrity and well-being of the species.
As a maturing, re-wilded, conservation area the removal of alien, invasive plant species and the remnants of old farming infrastructure is an on-going and intensive process.
An additional, significant conservation emphasis is placed on habitat expansion, community involvement, and long-term sustainability.
Wildlife Management
Our approach to species conservation is holistic and integrated, focussing not only on the health and safety of individual species but also on population dynamics, genetic diversity, and the socio-economic value of species within their ecosystems.
Rhino Conservation
In addition to the threat of poaching, there are many factors that place pressure on the survival of this species: habitat loss and fragmentation due to agricultural expansion, human settlement, and land development; genetic bottlenecks as animals are forced to live in smaller populations and natural mortality, which is inevitable.
Our rhino conservation efforts aim to minimise preventable deaths due to stress events during translocations, predation, and intra- and inter-species competition which lead to territorial conflicts. A key objective is to maintain genetic diversity through the timely translocation of sub-adult males to new habitats and the introduction of adults bulls for new genetics, when needed. These actions mitigate the risk of overpopulation and skewed sex ratios which can compromise the long-term survival and genetic heterogeneity of rhino populations.
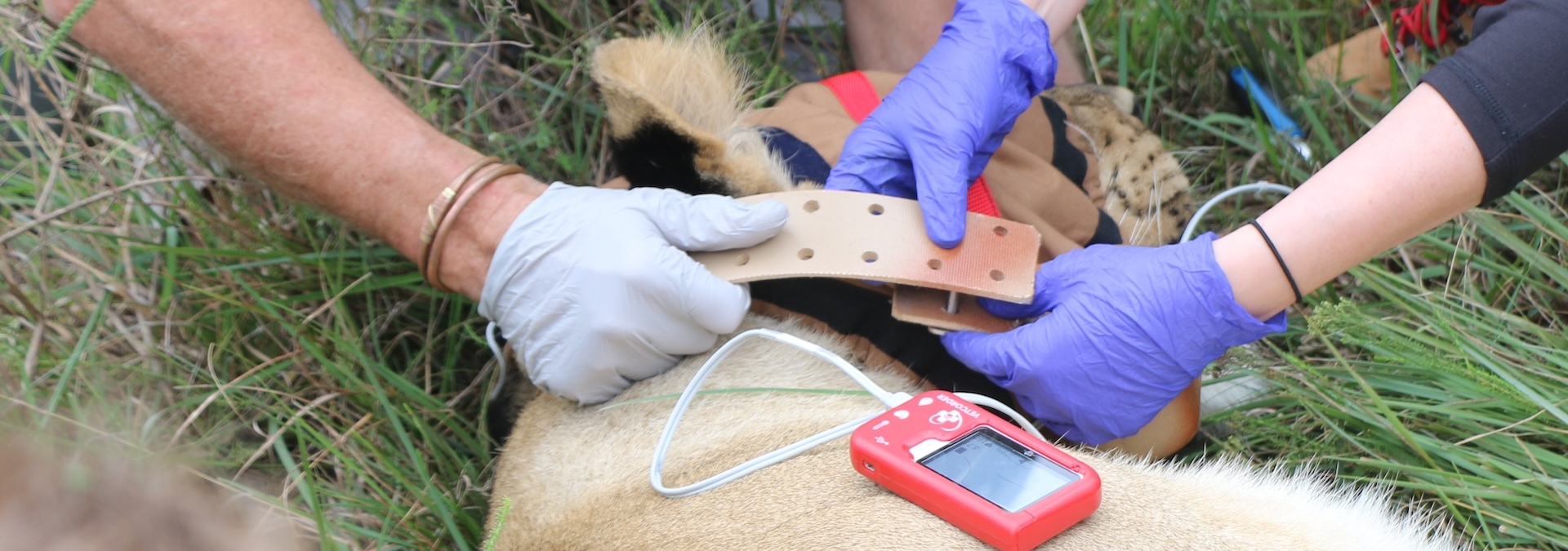
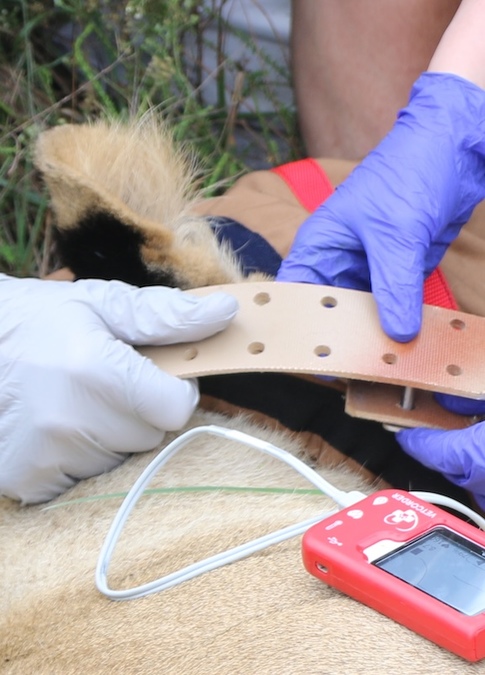
Lion Conservation
Lions face significant challenges due to habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and illegal hunting.
Our conservation objectives for a wild, managed, population of lion seeks to mimic natural processes, such as lion dispersal and predator-prey dynamics. To maintain a healthy predator-prey balance, detailed monitoring of lion behaviour, prey selection, and habitat use is conducted. We support land expansion projects to accommodate growing lion populations and ensure ecological balance. As with other conservation efforts, compliance with national norms and coordination with conservation institutions are integral to our lion management strategy.
Cheetah Conservation
Cheetahs face serious threats from habitat loss and fragmentation, which lead to increased human-wildlife conflict and reduced genetic diversity due to isolated populations. Conflicts with farmers and livestock owners are common as cheetahs' natural habitats shrink.
Managing cheetah populations in challenging terrains carries the risk of breakouts, which could lead to human-wildlife conflict. Additionally, cheetahs experience high mortality rates due to competition with larger predators like lions, leopards, and hyenas.
We aim to establish a cheetah population as a source population for reintroducing cheetahs into other protected areas. The creation of wildlife corridors to reduce habitat fragmentation is a key strategy to facilitate safe movement between habitats.
Elephant Conservation
Elephants are primarily threatened by poaching for their ivory and habitat loss due to human encroachment. Elephant overpopulation can lead to significant habitat degradation, with cascading negative effects on ecosystem health and species diversity. Maintaining intricate social structures and ensuring long-term genetic heterogeneity within elephant populations are complex tasks that require careful management.
We address these threats by increasing available habitats for elephants, facilitating the creation of wildlife corridors to mitigate human-wildlife conflict and enhance genetic flow between populations. Intensive monitoring of both the elephants and their habitat allows the conservation team to assess ecosystem health and ensure population stability.
Habitat Management - Alien Plant Control
As a result of the success of our education, youth development and skills development projects we have a dedicated team of Alien Plant Controllers working on the reserve daily.
All alien species within the 11, 500 hectare wilderness have been mapped using advanced technology and the team are deployed to work in identified areas clearing Wattle, Pine, Blue Gum, Red-eye, Port Jackson and two species of Cactus.
It is not enough to simply remove the plant. The team has revisit sites serval times to check for regermination and remove saplings before they take hold again.
How can you Help?
All help and support is hugely appreciated.
You can help in many ways:
- Book a Safari to Kariega Game Reserve and contribute via the levy donation.
- Join the Kariega Foundation Volunteer Programme.
- Pack for a purpose when you visit.
- Set-up a monthly, recurring donation.
- Donate to a project.
Contact us regarding other ways to connect and collaborate.
Donation Impact
Social and Emotional Learning
R300 - 1 learner per year
Youth Development
R1500 - per youth per year
Conserve Biodiversity
R2000 - 10 hectare per month
Save The Rhino
R7500 - per day
Join our volunteer programme
Research Projects
- Elephant social dynamics and animal health – Elephant Reintegration Trust (ERT).
- Effects of landscape expansion on elephant group associations, spatial utilisation & stress hormones - Bring The Elephants Home (BTEH).
- Black and White rhino monitoring focused on habitat selection, associations, habits, conditions, population dynamics, breakout and poaching risk.
- Lion monitoring focused on prey preferences, habitat selection, associations, population dynamics and breakout risk.
- Cheetah monitoring focused on prey preferences, habitat selection, interactions, population dynamics and breakout risk.
- Leopard research in partnership with NMU and other INDALO reserves on a PhD leopard study to help determine the region's population dynamics, range use and prey selection using camera trapping data.